STRUCTURE
5G-SMART is structured in five technical Work Packages (WPs), one work package for management and one work package for dissemination and exploitation of results. From the five technical work packages, three of them will focus on trials and validation, one will focus on the developing and prototyping conceptual features and another one will focus on mainly conceptual work in the business and technical aspects for different radio deployment options. The Figure below shows a brief overview of the WP structure and interactions between them.
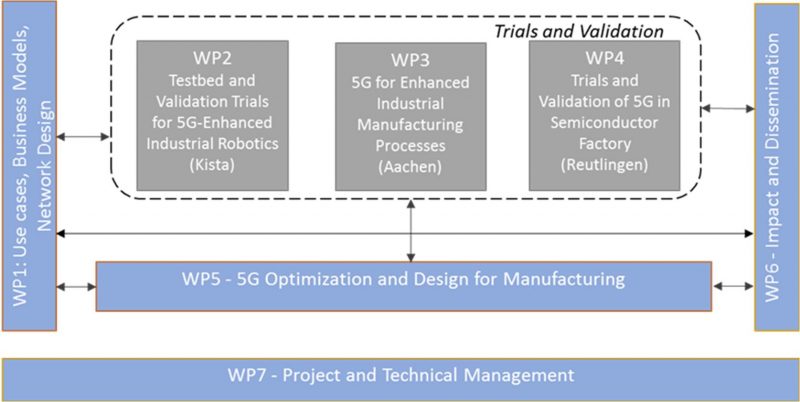
Figure 5G-SMART Work Package Structure
The main objectives of each WP are briefly described as follows:
- WP1 describes the use cases, their requirements and related KPIs as well as innovative and viable business models from the vertical industry perspective. Furthermore, this WP identifies and evaluates different network design options considering the technical use cases and business related KPIs.
- WP2 develops a 5G-based testbed located in an Ericsson smart factory in Kista, Sweden. This trial site focuses on 5G-enhanced mobile robotics.
- WP3 develops a 5G-based testbed located inside the shopfloor of the Fraunhofer IPT in Aachen, Germany. The trial investigates the potential of 5G for the enhancement of industrial manufacturing processes and its integration into the manufacturing environment. This WP focuses on critical process monitoring scenarios, that cannot be realized with state-of-the-art systems or directly benefit from the ubiquitous availability of a wireless connection.
- WP4 develops a 5G-based testbed in Reutlingen, Germany, where the focus is on enhancing a Bosch semiconductor factory with 5G, performing channel measurements and investigating Electromagnetic Compatibility.
- WP5 further leaps from the trials work-packages by diving deep into various technical aspects of the 5G systems beyond those that are already standardized (e.g. in the scope of 3GPP Release 15 specification) or currently under standardization. This WP designs and validates with prototypes some of the identified feature required in industrial applications beyond current technical solutions.
- WP6 is devoted to dissemination, exploitation, and standardization activities.
- WP7 provides the project and technical management.
